Triangle Review: Fundamentals of Triangle , Formula’s for Triangle , Types of Triangle , 45° – 45° – 90° Triangle , 30° – 60° – 90° Triangle , Congruent Triangles, Similar Triangles
Class Questions : Practice Examples 1, Practice Examples 2
Practice Questions : Exercise 1, Exercise 2, Exercise 3 , Exercise 4
________________________________________________________________________
Triangle_Review
The triangle is a three sided closed polygon with sum of interior angles measures equal to 180°.
Fundamentals of Triangle
-
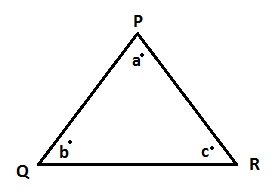
Line segment PQ, QR and PR are three sides of the triangle.
-
a°, b° , c° are the three interior angles of the triangle.
-
The third side should always be lesser than the sum of two sides of the triangle.
“The triangle will not complete and cannot make a closed polygon if one of the sides is greater than sum of other two sides”.
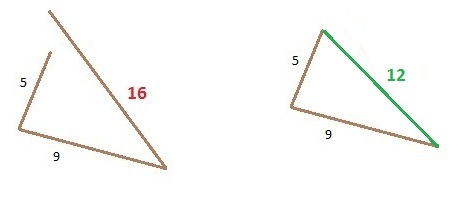
Example 1. As shown in the figure the triangle having two sides 9 and 5, the third side is 16 which is greater than 9 + 5 = 14.
Incorrect: 16> (5+9) Correct: 12< (5+9)
-
The third side should always be greater than the difference of two sides of the triangle.
“The triangle will not complete if one of the side is lesser than the difference of two sides”.
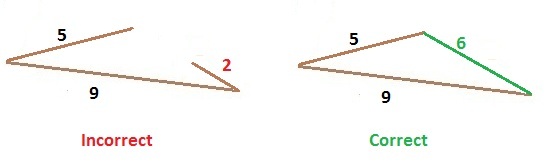
Example 2. Here in the below figure if two sides of triangle are 9 and 5, the third side is 2 which is less than the difference of 9 – 5 = 4.
2 < (9-5) 6 > (9-5)
-
The side opposite the largest angle is longest side of a triangle.
See below figure.
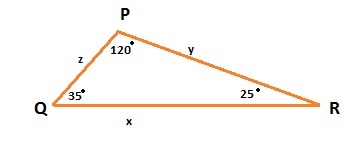
QR is the longest side of the triangle as it is opposite to largest angle of triangle. 2nd longer will be PR as 35° is greater than 25° . The PQ will be shortest side of ΔPQR.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>NEXT PAGE
Triangle Review: Fundamentals of Triangle , Formula’s for Triangle , Types of Triangle , 45° – 45° – 90° Triangle , 30° – 60° – 90° Triangle , Congruent Triangles, Similar Triangles
Class Questions : Practice Examples 1, Practice Examples 2
Practice Questions : Exercise 1, Exercise 2, Exercise 3 , Exercise 4