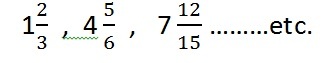Review : Basic Rules of Fraction , Types of Fraction , Special Fraction
The fraction is how many parts of a whole . It is being written as m/n . Where m is numerator and n is denominator,
both are integers and n ≠ 0.
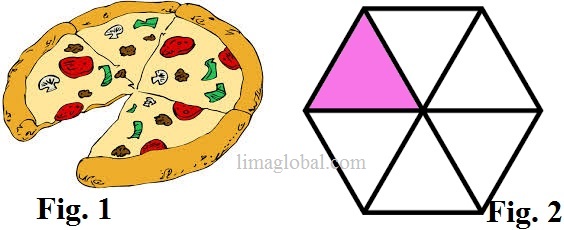
In above figure we can understand like ; Fraction 1/3 that is – one whole is divided into three parts and out of these three take one part.
Fraction 7/10 – One whole is divided into ten parts and out of these ten take 7 parts.
Now find out yourself what will be the fraction of following figures.
Basic Rules of Fraction
- If we multiply numerator ‘m’ and denominator ‘n’ with the same number the resultant will be equivalent to m/n .
Ex.1 5/6 = (5 x 3 )/(6 x 3) = 15/18 ; Ex.2 2/3 = ( 2x 4)/(3 x 4) = 8/12
- A fraction can be reduced to a lowest term by dividing numerator and denominator with same number.
Ex.1 12/64 = 3/16 ; Ex. 2 25/35 = 5/7
- Two add or subtract two fraction first take common denominator by taking LCM , and convert it to equivalent fraction.
Ex. 1 2/3 + 5/6
LCM of denominator 3,6 is 6
= (4 + 5)/6
= 9/6
= 3/2
Ex. 2 7/8 – 3/4
LCM of numerator 8 and 4 is 8
= (7 – 6)/8
= 1/8
- A negative sign in numerator or denominator will be written in front of fraction .
Ex. 1 -4/5 = -4/5 Ex.2 6/-7 = -6/7
- Multiplication of two fractions can be done directly by taking product of numerator and denominator.
Ex. 1 (2/3) x (1/2 ) = (2 x1 )/ ( 3 x 2 ) = 2/6
Ex. 2 (-4/7) x (2/8) = – 8/56
- To divide one fraction with another fraction first revert the second fraction ( or take reciprocal inverse of second fraction )and then multiply with first fraction.
Ex. 1 7/9 ÷ 4/3 = 7/9 x 3 /4 = 7/12
Ex. 2 – 9/15 ÷ 1/3 = (- 9/15) x (3/1) = -9/5
Types of Fraction
- Proper Fraction – When numerator is smaller than denominator then we call the fraction as proper fraction
2/5, -4/9 , 1/2 , 5/6 …etc
- Improper Fraction – When numerator is equal to or bigger than denominator than we say it as improper fraction.
5/2 , 9/5 , -6/5 , 7/3…… etc.
- Mixed Fraction – The combination of a whole number and the proper fraction is Mixed Fraction.
- Like Fraction – Fractions with same denominator is known as Like Fractions.
2/7, 5/7, 1/7 , 11/7, 18/7 125/7 ……………etc.
- Unlike Fraction – Fractions with different denominators are known as Unlike Fractions.
2/3, 7/9 , 35/6 , 2/11, 5/18 …………..etc.
Special Fractions
When for any fraction m/n ; ‘m’ and ‘n’ are not integers and n ≠ 0, we manipulate the expression as fractions only .
Ex. 1 a/2 + a/ 3 = (3a + 2a) / 6 = 5a/6
Ex. 2 √3 / 5 ÷ 2/ √3 = √3 / 5 x √3 /2 = 3/10
Ex. 3 π/6 + π/2 = ( π + 3 π) / 6 = 4 π/6 = 2 π/3