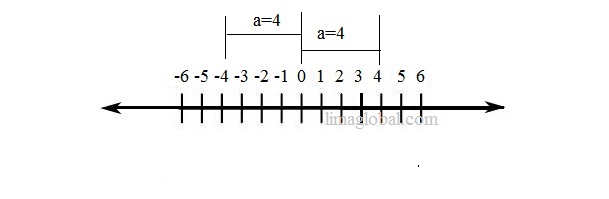Real Numbers Math Arithmetic
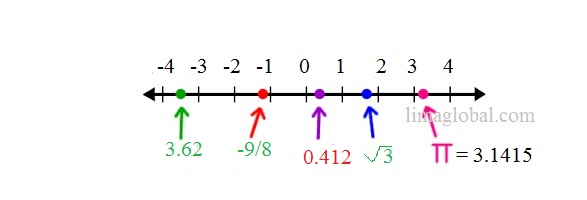
The Real numbers includes all whole ( 0 ,1 , 2, 3, ,4 ,5 ,6 ….) rational (-5, -6, -9 , 3/5/ 7/8 ……) and irrational ( √2 =1.41421356 , √3 = 1.7320508 , π = 3.1415) numbers. It can be positive, negative and zero.
The real numbers can be represented on number line known as Real Number Line.
The infinite and imaginary numbers are not real numbers like √ -1 = Imaginary or (No value ) .
Greater than ‘>’
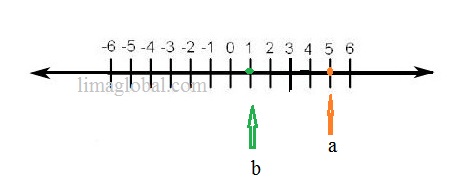
If any real number ‘a’ is greater than another real number ‘b’ than ‘a’ will be on the right side of the ‘b’ on the number line . a>b.
Ex. 1
If a=5 and b = 1
Lesser than ‘<’
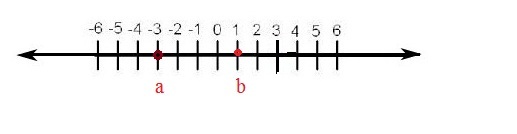
If any real number ‘a’ is lesser than another real number ‘b’ than ‘a’ will be on the right side of the ‘b’ on the number line . a < b
Ex. 1
If a= -3 and b = 1
Interval
When we write like 2 < x < 6 that means ‘x’ is having the value in between 2 and 6.
As we all know that there are four intervals with one end point.
< Less than
> Greater than
≤ Less than or equal to
≥ Greater than or equal to
Absolute Value
The absolute value of any number ‘a’ is its distance from zero. The symbol is “│ │” .
Whether number is on positive side of number line or negative side of number line . The result will always be positive.
│a│ = a and │-a│ = a
If a = 4 than │4│ = 4 and │- 4 │ = 4
But when the negative sign is outside the absolute symbol than
-│a│ = – a
Some More Rules
- │a + b │ ≤ │a│ + │ b │
2. │a│ x │b│ = │a x b│
Examples
- │5│ = 5
- │-5│ = 5
- -│5│ = -5
- -│- 5│= – (5) = -5
- │0│ = 0
- │-2 x 7│ = 14
- -│ 8 – 3│ = -5