Integer Review: Fundamentals of Integers , Rules for Multiplication , Rules for divisibility, Division Terminology, Even & Odd Integer, Rules about even & odd integer, Prime Number, Prime Factorization , Distinct Prime Number, LCM & HCF, Composite Numbers , Consecutive Integers
Class Questions : Exercise 1 Exercise 2 Exercise 3 Exercise 4 Exercise 5
Practice Questions : Solutions
____________________________________________________
Multiple of Integer
Increasing any integer with the same amount is multiple of an integer.
Like, Multiple of 5 = 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35……………………..
3 = 6, 9, 12, 15, 18…………………………….
12 = 24, 36, 48, 60………………………….
Factorization of Integer
Reducing any integer up to its prime number is factorization of integer.
Like, Factors of 12 = 2 x 2 x 3
15 = 3 x 5
LCM – Least Common Multiplier
This is useful in addition and subtraction of fractions; The LCM of any two non-zero integers ‘x’ and ‘y’ is least positive number which is multiple of both x and y.
e.g. Find LCM of 12 and 18.
So LCM of 12 and 18 will be =
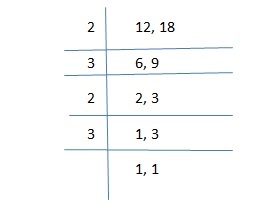
LCM = 2 x 3 x 2 x 3 = 18
HCF – Highest Common Factor
It is also known as greatest common divisor. For any two or more positive integers x, y and z; HCF is the highest common number which can divide all of them.
As for example;
Example 1. Find the HCF of 12, 48 and 78?
Solution;
First find out the prime factors of numbers
12 = 2 x 2 x 3
48 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 3
78 = 2 x 3 x 13
Now see the common number among 12, 48, and 78 are 2 and 3 only.
So, HCF = 2 x 3 = 6. Here ‘6’ is the highest common integer which can divide all 12, 48 and 78.
